Generative AI assistants are becoming more proficient at:
- Creating an outline for a paper, or bullet points and graphics for slides
- Writing longer coherent prose in multiple languages
- Critiquing a written passage, editing text, and correcting computer code
- Providing explanations or ideas for a literature review with mostly accurate citations
- Summarizing longer articles, text, or a corpus of texts
- Suggesting a response to a question, such as on a short answer or multiple-choice test, or for a discussion board posting
- Translating text more accurately
- Creating images and videos from images and text
- Creating computer code in multiple languages
- Developing entire online courses from beginning to end including assignments, videos, resources and activities
- Assisting users with formulas inside applications such as Excel
These are only some examples. We recognize that some instructors may want to allow, or even encourage, their students to use these technologies, and others may want to curtail their use. Consider these six areas below before you create language for your assessments.
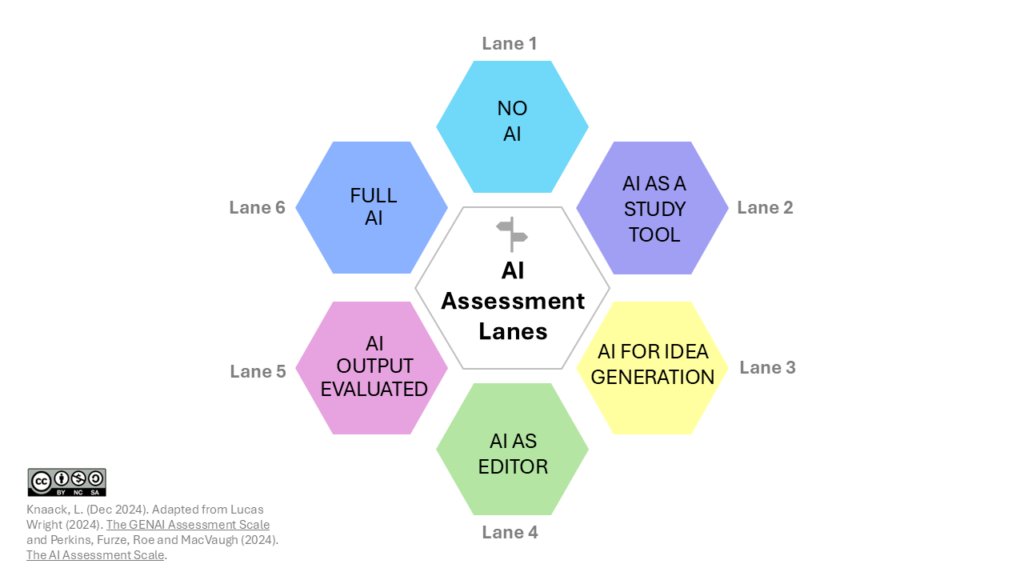
Following is a chart of six lanes of how GenAI can be an assistance to you in your learning. Please note which course assessments fall under each level.
LANE |
StUDENT EXPECTATIONS |
NOTES FOR INSTRUcTORS: DO NOT INCLUDE FOR STUDENTS |
NO aiAI Must Not Be Used
|
|
This lane is used when you want full original demonstration of student learning that aligns with the learning outcomes without the use of AI tools. This lane is idea for testing core knowledge and comprehension. Examples:
|
AI as A STUDY TOOL
AI Used as a Study Companion or Tutor |
|
This lane is for being clear with students that they are allowed to use AI as a study mechanism. Given that you are unable to monitor out-of-class activities, you would use this lane for an assessment to be clear with students about the use of AI for studying. You may practice use of this in class, share how to write prompts to have GPTs act as a tutor or point out tutors that have been developed to provide study supports. |
AI FOR IDEA GENERATION
AI Used to Enhance Brainstorming |
|
This lane is when you are okay with students getting ideas and generating possible directions using GenAI as they may already do with friends, family and search engines. This lane is suitable for assessments for demonstrating writing skills. Students may use AI tools to generate ideas for an essay or report. AI may provide student assistance in getting started, expanding on initial thoughts or providing other perspectives. |
AI as EDITOR
AI Provides Feedback for Improvement |
|
This lane is used when you want the students to produce original work, but they can use GenAI tools to edit, get feedback on areas for improvement and create citations and references. GenAI acts like an editor. |
AI OUTPUT EVALUATEDAI Results are Critically Evaluated |
|
This lane is useful when you want students to develop a deeper level of engagement with course materials, undertake more independent learning and developing skills involved in evaluating the information produced in this GenAI era. You would choose assessments where you want to see student analyses of AI results, comparisons of other data sources, exploring what is true and not true, etc. |
FULL AIAI is Integral to Assessment |
|
This lane is used when the AI output/submission may use previously created original work.
Examples of assessments might include: input notes from a group discussion to generate a summary, production of themes from a number of individual presentations, collating research findings into a summary report, students submitting original design concepts for a proposed urban planning scenario and having AI generate a visual representation of those ideas etc. |
Students: Be aware of limitations and issues with using GenAI, such as the following:
- If you provide minimum-effort prompts, you will get low-quality results. You will need to refine your prompts to get good outcomes. This will take work.
- Almost all GenAI tools sit on servers outside of Canada and if you require an account your personal identifiable information will be stored and accessed by many organizations. Many GenAI tools also require a fee or a subscription or provide a limited free account and any upgrades to more tools requires payment that you must pay for.
- A protected version of Microsoft Copilot is available to all students, faculty and staff through North Island College’s Microsoft Office license. This is the most secure tool to use. If you use other tools, anything you upload, type in or submit to the tool may be used by that tool or others to train GenAI. Be careful.
- Do not trust anything GenAI says. If it gives you a number or a fact, assume it is wrong unless you either know the answer or can check with another source. You will be responsible for any errors or omissions provided by the tool. It works best for topics you understand.
- GenAI is a tool, but one that you need to acknowledge using. Please include a reflective summary at the end of any assignment that uses AI explaining what you used the AI for and what prompts you used to get the results.
- Be thoughtful about when GenAI is useful to you in your learning. Do not use it if it is not appropriate for the case or circumstance.
NOTE: A protected version of Microsoft Copilot is available to all students, faculty and staff through North Island College’s Microsoft Office license. However, other generative AI applications may require registration and/or a subscription fee and personal information for an account will most likely be hosted on a server outside of Canada and privacy of personal data is needing to be noted. Please consider offering students a choice to opt-out of using a system other than the protected version of Microsoft Copilot if they have concerns about the cost, privacy, security or other issues related to the technology.
For simplicity, when the word assessment is used in the chart below it could mean either the formal or informal components of assessment. The word assessment can mean two things: 1) a formal evaluation of learning that is assigned a value (mark, grade, level) that contributes to the final grade. (e.g., a test, project, assignment, exam, assignment) and 2) informal engagement of learning that is not assigned any value (mark, grade, level) contributing to the final grade (e.g., a discussion, quiz, readings, group activity etc.)
The following suggested statements are intended to help you shape the message you provide to your students on a course outline as well as on your assignment instructions to reinforce a shared understanding of what is, and is not, allowed in your course.
- Inspired by work of those listed in the credits (below), aligned to learning outcomes and enhanced by Liesel Knaack, Director, Centre for Teaching and Learning Innovation, North Island College (December 8, 2024)
NOTE: As our understanding of the uses of AI and its relationship to student work and academic integrity continue to evolve, students kindly discuss your use of AI in any circumstance not described here with me to ensure it supports the learning outcomes for the course. Students, you are to act ethically and professionally at all times in alignment with NIC Policy 3-06, Community Code of Academic, Personal and Professional Conduct (Code of Conduct). If attribution of generative AI work is required consult MLA Style Guide 9th Edition – Creating References for Artificial Intelligence (NIC Library website)
Attribution
The work was inspired and developed from the already amazing work done by these educators around the world specifically these listed below:
- Wright, L. (2024). The GenAI Assessment Scale.
- Furze, L (August 28, 2024). Updating the AI Assessment Scale.
- Furze, L. (May 20, 2024). The AI Assessment Scale in Action: Examples from K-12 and Higher Education Across the World
- Furze, L. (May 23, 2024). The AI Assessment Scale GPT: Aligning your Assessment with the AIAS
- Furze, L. (Dec 18, 2023). The AI Assessment Scale: Version 2
- Perkins, M., Furze, L., Roe, J., MacVaugh, J. (2024). The Artificial Intelligence Assessment Scale (AIAS): A Framework for Ethical Integration of Generative AI in Educational Journal of University Teaching and Learning Practice, 21(6).https://doi.org/10.53761/q3azde36
- Liu, D. (April 2024). University of Sydney – Menus, Not Traffic Lights: A different way to think about AI and assessments
- Bridgeman, A. & Liu, D. (July 2024). University of Sydney – Frequently asked questions about the two-lane approach to assessment in the age of AI
- Steel, A. (July 2024) Director AI Strategy, Education, UNSW Sydney in 2 lanes or 6 lanes? It depends on what you are driving: Use of AI in Assessment
- Teaching and Learning Services, Carleton University in Generative Artificial Intelligence: Recommendations and Guidelines, October 4, 2023